on
BY SIMONE J. SMITH
CONSUMER ALERT! CONSUMER ALERT!
In presenting the information about electric vehicles in this article, it is important to acknowledge that certain readers, particularly enthusiasts and fans of electric vehicles, may find aspects of the content challenging, or even disagreeable. Our responsibility, however, is to provide accurate and unbiased information to our readership.
While some may hold strong preferences for electric vehicles, it is our commitment to present the facts surrounding them objectively. It is through a fair and comprehensive examination of the subject matter that we aim to foster informed discussions and empower our audience with the knowledge needed to make well-rounded decisions in the rapidly evolving landscape of automotive technology.
Now, let’s start with a couple stories; a gentleman set off on a road trip to Halifax in his new Ford F-150 extended range vehicle. He topped up his charge in Nipigon and Terrace Bay, but the Petro-Canada app listed the company’s chargers in Marathon in Wawa as out of service. He decided to get his car juiced up instead at the Ivy charger in White River, but when he got there, he discovered the charger was down too.
Our next story is about the owner of a 2023 F-150 Lightning Lariat. First, it’s worth noting that he bought the truck new for approximately $88,000 before taxes, so it’s understandable he had great expectations about it.
While he liked how the electric pickup drives and the fact it is very roomy and luxurious for a truck, there were several things that cast a shadow on his ownership experience. He often had difficulty: charging the vehicle on his drives outside the city and finding fast chargers that worked and weren’t backed up with people waiting to charge.
He also had issues with the main interface, which he said was not very user friendly despite Ford recently updating it to the latest Sync 4 version. He complained about poor phone call quality and the fact the interface did not default back to the map when driving, among other things.
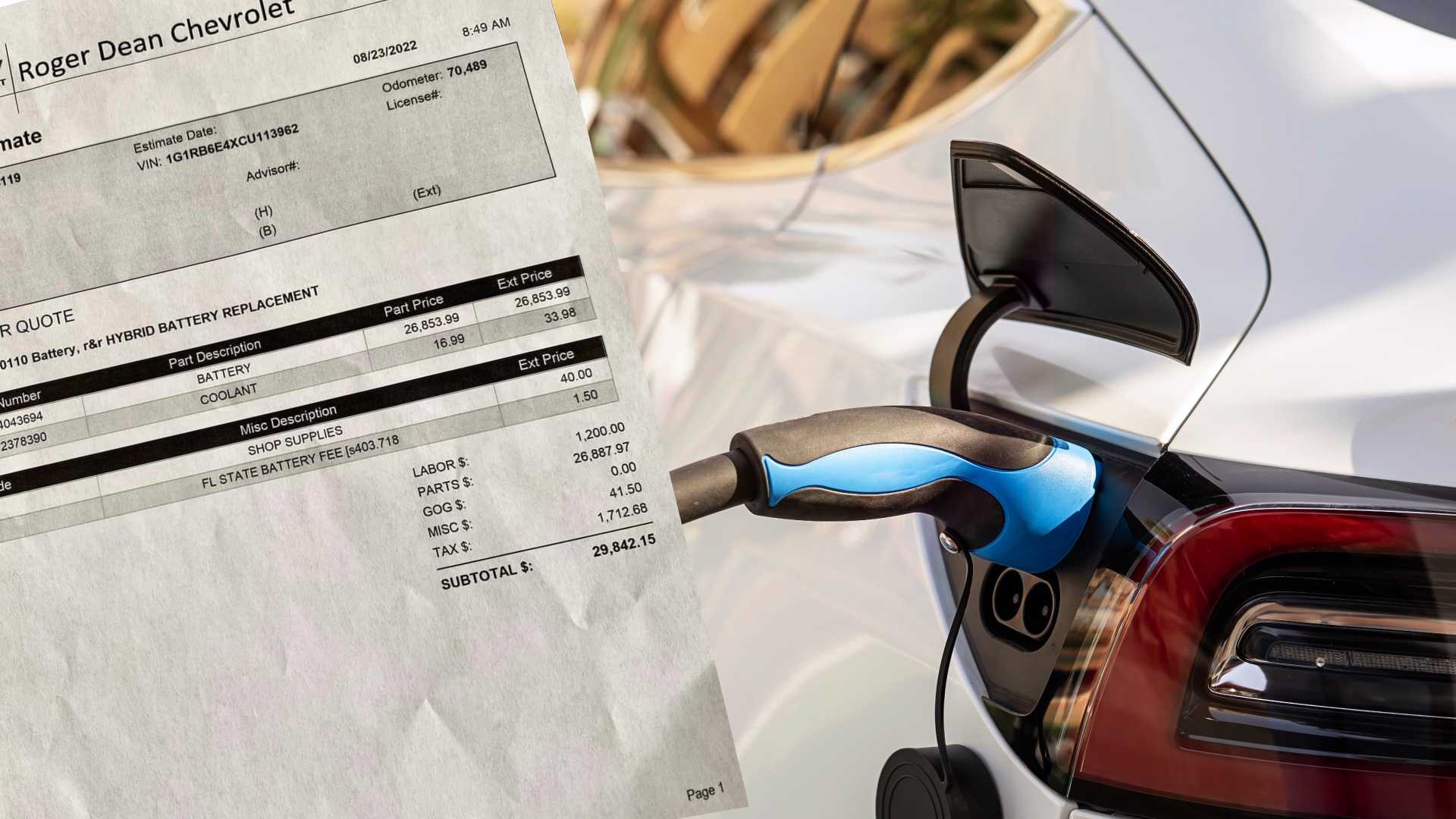
My last story is about an EV owner who had to replace his battery. When he brought his car into the dealership, they looked up the replacement battery cost online and the dealership told him, “You’re not going to like this.” It was about $15,000 for the battery plus labour and taxes. The owner of the vehicle felt like it was not worth it to invest $20,000 in a car that was now over ten years old.
As electric cars and trucks have gone mainstream, they have faced a persistent question: Are they really as green as advertised, and are they worth the money?
A survey published in July, 2023 by J.D. Power found only around a third of Canadians were considering EV’s as their next vehicle purchase, and that number was trending downward. Those who rejected EV’s cite limited range, and lack of charging stations as key reasons. The growth of electric vehicle sales has since slowed sharply. In June 2022, EV sales were growing about 90% year over year. By June of 2023, the 12-month growth rate had slowed to about 50%, and automakers had become increasingly fearful that the pace would weaken further.
What are the reasons for this? There are a few, so please bear with me.
First of all, owners of electric cars will most likely pay more for insurance. Canadian EV owners can expect higher insurance costs in the future. One of the factors is that they cost more, so simply because they cost more, they’ll be more expensive to insure. The higher the value, the higher the cost is to replace if the car is damaged or stolen. It is a risk that the insurance companies will factor into their pricing.
Then there are the costs to replace battery packs, the availability of replacement parts and the scarcity of skilled technicians, all that affect the price of repairs and ultimately insurance rates in the short run.
An October 28th, 2023, Financial Times article stated that British auto insurers increased their rates considerably over the year, with carriers suspending insurance coverage for EVs altogether to enable it to re-evaluate the cost repairs. Also, recent media reports from British Columbia described how the main provincial auto insurer wrote off an entire EV, because to replace the battery would be the same as buying a new car of the same brand and make. Some electric car owners, especially those with earlier models, have been shocked to find out how much it costs to replace their batteries.
Then you have to consider the fact that a higher number of EV’s on the roads inevitably means more of them becoming involved in accidents. There is widespread anxiety over dinged-up batteries since they could in theory compromise the safety of the vehicle, causing: electric shocks, fires, and even explosions. Fires remain extremely rare, though, and are less common on average than in internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
There are defenders of EV’s who have snapped back against the media that they say spreads misinformation about this budding technology. Some media critics have stated that whenever an EV has a problem that apparently is news, but when thousands of gas cars can’t start in the cold or catch fire on the side of the road — well, that’s just life. For some, misinformation about EV’s has become such an issue that the U.K. ‘s House of Lords urged the government to push back against EV misinformation in the British press.
We can’t completely ignore companies like Tesla, whose charging network is the largest on the continent and known for its reliability. It has been reported that EV’s of all stripes will soon have access to Tesla’s robust network as the company’s charging port is fast becoming the North American standard.
I get it; it is new technology, and like anything new, there will be kinks, but it cannot be ignored that EVs may have more problems than conventional cars. Electric vehicles have proved far less reliable, on average, than gasoline-powered: cars, trucks and SUVs. According to a 2023 survey by Consumer Reports, EVs from the 2021 through 2023 model years encountered nearly 80% more problems than did vehicles propelled by internal combustion engines.
The reports said EV owners most frequently reported troubles with battery and charging systems as well as flaws in how the vehicles’ body panels and interior parts fit together. The magazine and website noted that EV manufacturers are still learning to construct completely new power systems, and it suggested that as they do, the overall reliability of electric vehicles should improve.
Like many other batteries, the lithium-ion cells that power most electric vehicles rely on raw materials — like cobalt, lithium and rare earth elements — that have been linked to grave environmental and human rights concerns. Cobalt has been especially problematic. Mining cobalt produces hazardous tailings and slags that can leach into the environment, and studies have found high exposure in nearby communities, especially among children, to cobalt and other metals. Extracting the metals from their ores also requires a process called smelting, which can emit sulfur oxide and other harmful air pollution.
There are many other examples of the emerging problems that come hand in hand with the electrification of cars. While producing an electric car, manufacturers still end up emitting greenhouse gasses into the air.
We have more serious issues. Most of the greenhouse gasses come from aircraft, ships, and heavy traffic vehicles as well as from anti-environmental energy-producing technologies like coal-based thermal power plants.
Although they are marketing the EV as a step in the right direction to decrease climate change, there are obviously challenges that were not conceived, or are being ignored. Before making the decision to go electric, we need to really look at how this technology is serving us, and if we are yet again being taken on a propaganda ride.
REFERENCES:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19486963/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959652618335340
https://www-bbc-co-uk.cdn.ampproject.org/c/s/www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-68130432.amp
https://www.ntsb.gov/safety/safety-studies/Pages/HWY19SP002.aspx
https://www.jdpower.com/business/press-releases/2023-canada-electric-vehicle-consideration-evc-study
https://insideevs.com/features/503689/mustang-mach-e-infotainment-review-guide/
https://www.euronews.com/next/2023/12/26/we-cant-save-the-world-with-electric-cars
https://insideevs.com/news/670422/ford-f150-lightning-owner-explains-sold-6-months/
https://www.wired.com/story/ev-repair-batteries-expensive-insurance/
EV owners likely to pay more for insurance, report says. Here’s why
Rooftop Solar Could Meet 100% of Electricity Needs in Canadian Homes—Technically
Stay in the loop with exclusive news, stories, and insights—delivered straight to your inbox. No fluff, just real content that matters. Sign up today!
We, as humans are guaranteed certain things in life: stressors, taxes, bills and death are the first thoughts that pop to mind. It is not uncommon that many people find a hard time dealing with these daily life stressors, and at times will find themselves losing control over their lives. Simone Jennifer Smith’s great passion is using the gifts that have been given to her, to help educate her clients on how to live meaningful lives. The Hear to Help Team consists of powerfully motivated individuals, who like Simone, see that there is a need in this world; a need for real connection. As the founder and Director of Hear 2 Help, Simone leads a team that goes out into the community day to day, servicing families with their educational, legal and mental health needs.Her dedication shows in her Toronto Caribbean newspaper articles, and in her role as a host on the TCN TV Network.